画像をダウンロード enhanced greenhouse effect definition geography 155576
Geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only This information should not be considered complete Aerosols have a profound impact on the climate because, just like greenhouse gases, they are able to change the Earth's "radiative", or energy, balance Aerosols can control how much energy from the sun reaches the planet's surface by changing the amount that is absorbed in the atmosphere and the amount that is scattered back out to space greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4) and nitrogen dioxide (N 2 O), and a rise in these gases has caused a rise in the amount of heat from the sun withheld in the Earth's atmosphere, heat that would normally be radiated back into space This increase in heat has led to the greenhouse effect, resulting in climate change
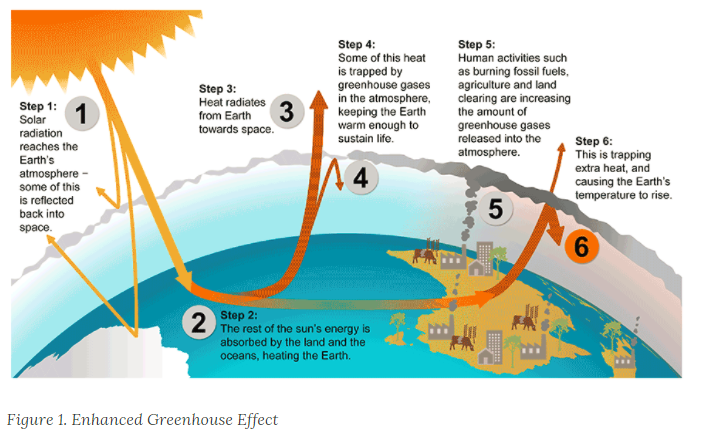
Day 2 9 3 9 5 Ap Environmental
Enhanced greenhouse effect definition geography
Enhanced greenhouse effect definition geography- Greenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many yearsThe warming effect of trace gas greenhouse gas is enhanced by the effect of water vapour, which also absorbs infra red radiation, leading to an important natural feedback effect between anthropogenic greenhouse gas and water vapour (Figure 111)




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society
Global warming is attributed to the enhanced greenhouse effect This is caused by the increased concentration and effect of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane and fluorocarbons JohnR Or for a bit more wasted heat, the extremely long discussion (>350 comments, unfortunately mostly circular in topic) at Waste heat vs greenhouse warming And, as muoncounter pointed out, about 1% of greenhouse gas warming, a forcing of ~0028 W/m^2 waste heat compared to 29 W/m^2 greenhouse effect forcingIf one applies this definition of scale to environmental phenomena equal parts of the enhanced greenhouse effect16 Over time, some CO 2 molecules are absorbed by plants, some by the oceans, some by the soil, greenhouse gases enhance the greenhouse effect is indifferent to such geographical specifics Temporally, the grain is likewise
Carbon dioxide and some other gases in the planet's atmosphere can absorb the infrared radiation emitted by the planet's surface as a result of exposure to solar radiation, thusAs the enhanced greenhouse effect The naturally occurring greenhouse effect traps the heat of the sun before it can be released back into space This allows the Earth's surface to remain warm and habitable Increased levels of greenhouse gases enhance the naturally occurring greenhouse effect by trapping even more of the sun's heat, resulting in a global warming effectEGE Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Looking for abbreviations of EGE?
Although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount ofAtmospheric science greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases Increasing enhanced greenhouse effect observed at the Earth's surface Over an 11 year study, the first observations of an increase in carbon dioxide at the Earth's surface has been made Whilst many studies of the quantity of co2 in the Earth's atmosphere is measured at high atmospheric levels, recent studies have been looking at the co2




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
See radiation, greenhouse effect, enhanced greenhouse effect, global warming 1 Intergovernmental Panel on climate Change (IPCC) The IPCC was established jointly by the United Nations Environment Programme and the World Meteorological Organization in 19 The purpose of the IPCC is to assess information in the scientific and technicalDeforestation is ongoing and is shaping climate and geography Deforestation is a contributor to global warming, and is often cited as one of the major causes of the enhanced greenhouse effect Tropical deforestation is responsible for approximately % of world greenhouse gas emissionsAge range 1114 Adapted and developed for top set KS3 group Students will learn about the greenhouse effect as a natural process;



7 H The Greenhouse Effect
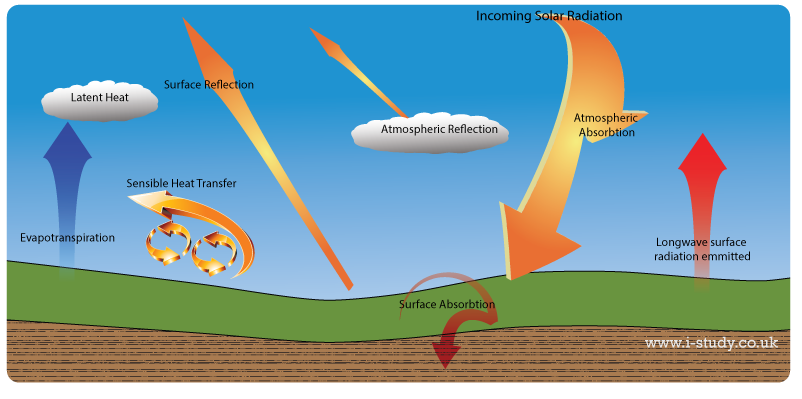



Ib Geography Environmental Sustainability
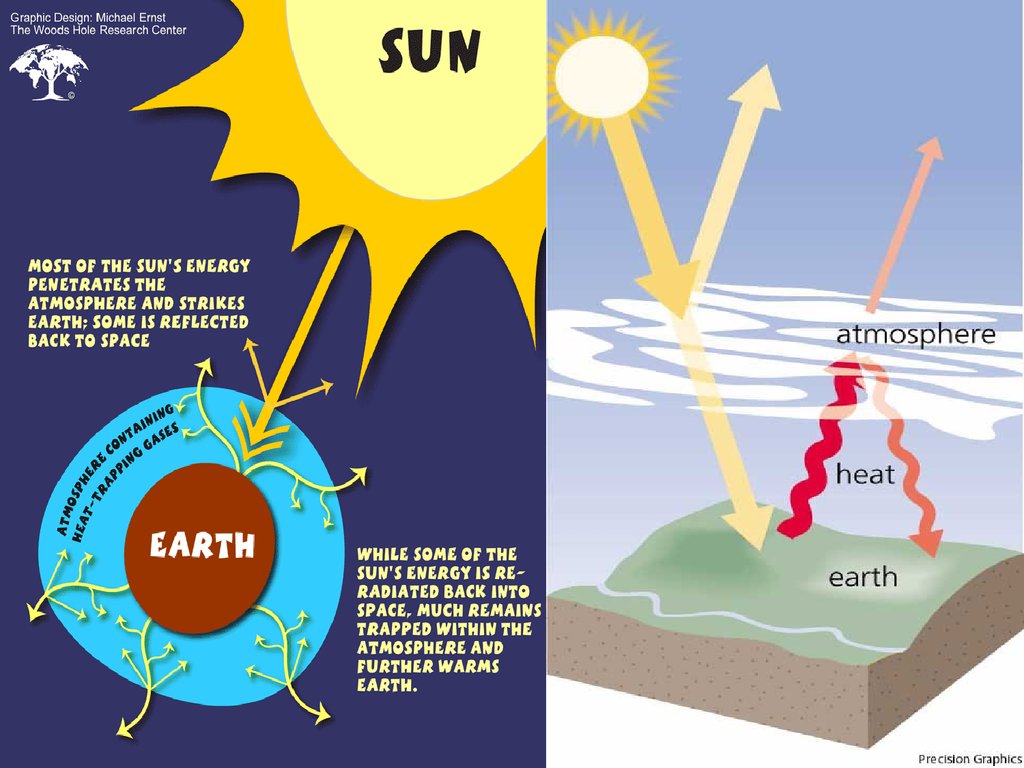
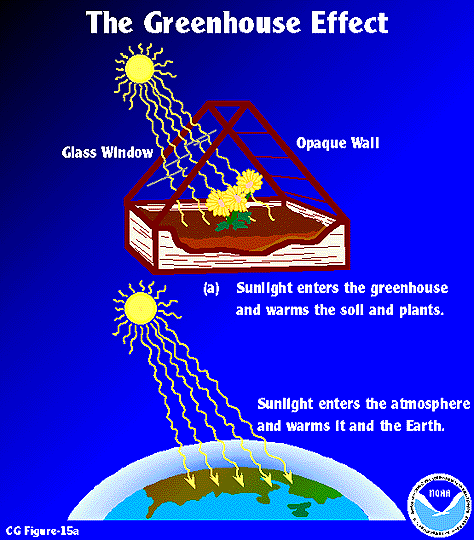
The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect"Enhanced greenhouse effect Y The trapping of heat radiation around the Earth by excess greenhouse gases produced through human activity Explosivity Y A measure of the relative explosiveness of volcanic eruptions varying due to formation on convergent or divergent boundaries Greenhouse gases Human activities such as energy, industry,Contrasts Enhanced greenhouse effect is due to human activity Greenhouse effect is a natural process Enhanced greenhouse effect = less energy escapes back into space & increases earth's temperature by 018⁰C every decade Enhanced greenhouse effect = levels of gases in atmosphere, especially CO2 have increased à'blanket




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
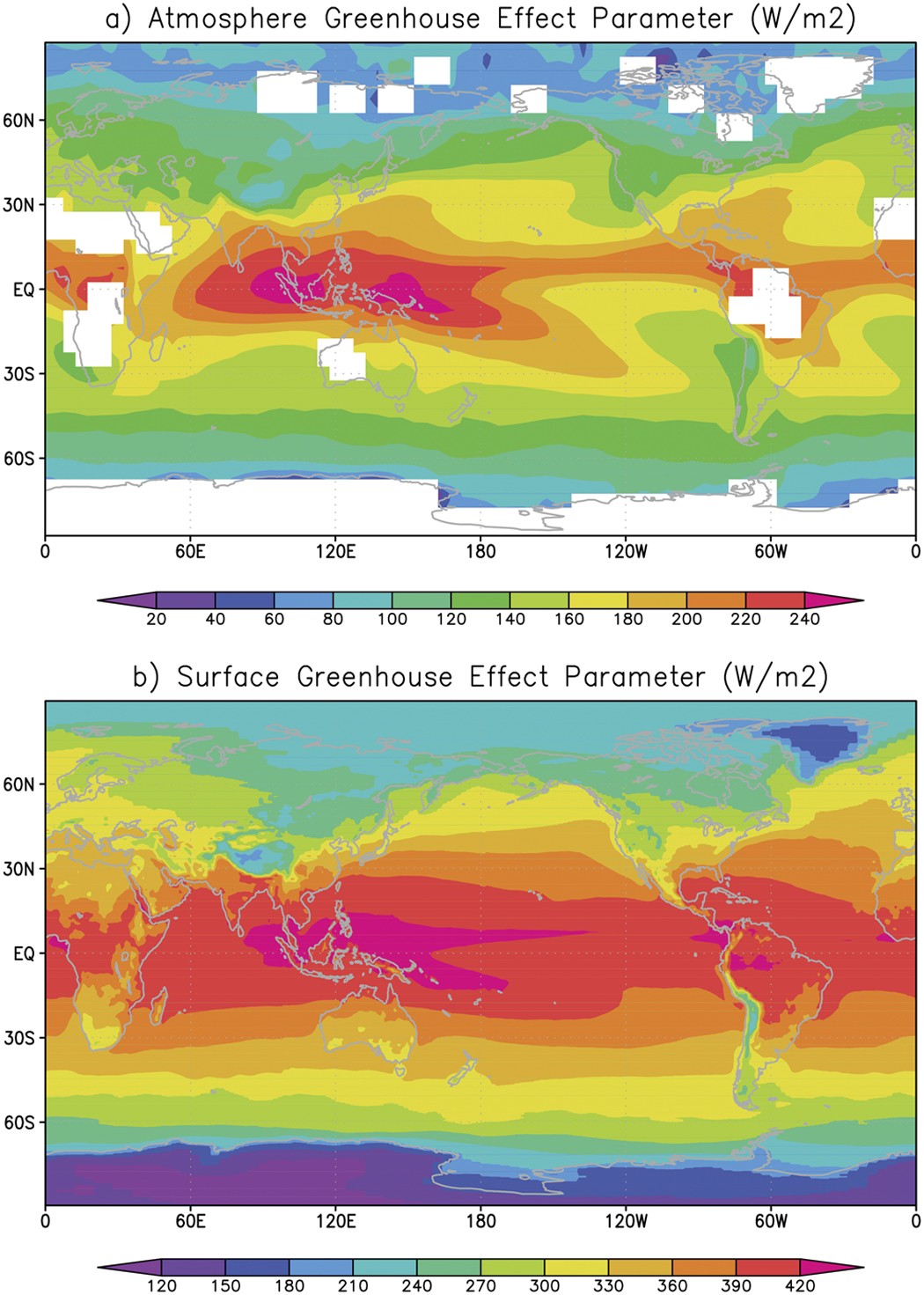



A Hiatus Of The Greenhouse Effect Scientific Reports
In this unit we will be looking at arid and equatorial climates as well as both the natural and enhanced greenhouse effect We will also be looking at the consequences on humans of the enhanced greenhouse effect There are 6 lessons in this unit with an end of unit exam at the endAnthropogenic global warming is a theory explaining today's longterm increase in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere as an effect of human industry and agriculture For well over a century, scientists have been concerned that as the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases, so will the planet's capacity to retain heat Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, and




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
How the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environmentIt absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocksThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existIndeed, the main culprit is, as we might have expected, CO 2 In terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share
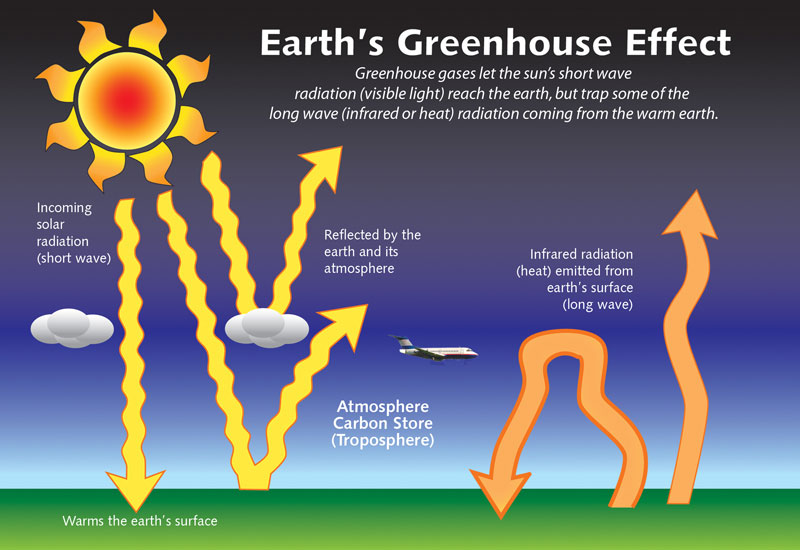



2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change Dp Geography At Nis




Global Warming
The enhanced greenhouse effect and climate change The disruption to Earth's climate equilibrium caused by the increased concentrations of greenhouse gases has led to an increase in the global average surface temperatures This process is called the enhanced greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapA major component of anthropogenic climate change is global warming, which refers to a gradual warming of the earth caused by an unnatural (humaninduced) increase of the greenhouse effect, as concentrations of greenhouse gases increase primarily from the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas)




Natural Greenhouse Effect And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Earth Planet S Atmosphere And Solar Radiation Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society
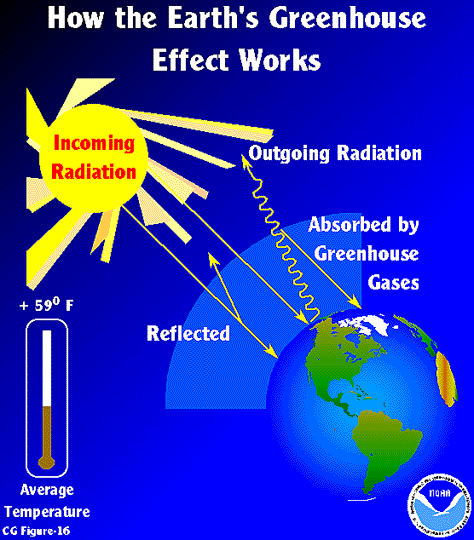
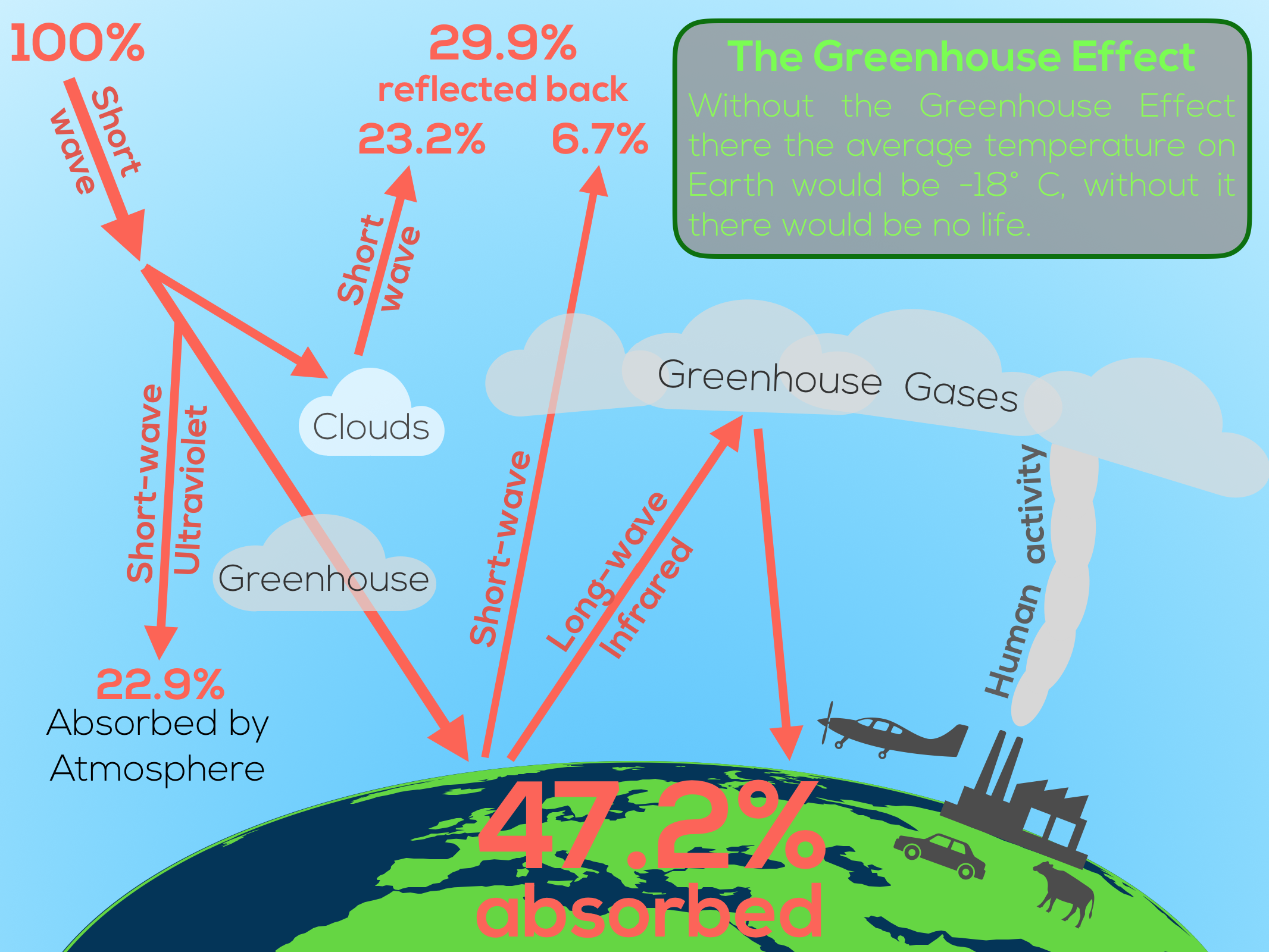
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Definition of greenhouse effect warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back toQuantitative analysis Energy flows between space, the atmosphere, and Earth's surface, with greenhouse gases in the atmosphere capturing a substantial portion of the heat reflected from the earth's surface The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this




Natural Greenhouse Effect Human Enhanced Greenhouse Stock Vector Royalty Free




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
How humans contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect and have the opportunity to offer possible solutionsThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat Yes, by increasing the abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, human activities are amplifying Earth's natural greenhouse effect Virtually all climate scientists agree that this increase in heattrapping gases is the main reason for the 18°F (10°C) rise in global average temperature since the late nineteenth century




Ppt Global Issues Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
The Greenhouse Effect Earth is much colder than the sun, but it is warmer than the space outside its atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is made up of gases, andGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear DOI / Comprehensive overview of many of the key themes in Brian Massumi's oeuvre, whose work has been seminal to theories of affect The text is particularly significant for understanding the mobilization of affect in regimes of power Pile, S "Emotion and Affect in Recent Human Geography"



What Is The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect What S Your Impact



1 Causes Of Climate Change
The problem is that our increased release of greenhouse gases is causing an increase in the greenhouse effect called the enhanced greenhouse effect This isContext The natural greenhouse effect makes our planet livable, but human activities are creating an enhanced greenhouse effect that is changing global climate Gulf Stream Definition major current in the Atlantic Ocean that carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico up the coast of North America and toward Europe As the fossil fuels burning increased, the ration of carbon dioxide in the surroundings has majorly enhanced hence it adds up to the Greenhouse




6 3 The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Climate Change Organization




The Greenhouse Effect R Electromagnetic Em Radiation Radiation
2 (Physical Geography) the application of this effect to a planet's atmosphere;It is the process by which absorption and emission of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases warm a planet's lower atmosphere and surface Naturally occurring greenhouse gases have a mean warming effect of about 33 °C (59 °F), without which Earth would be uninhabitableTo further complicate matters, cloud properties may change with a changing climate, and humanmade aerosols may confound the effect of greenhouse gas forcing on clouds With fixed clouds and sea ice, models would all report climate sensitivities between 2° ;C and 3°C for a




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp




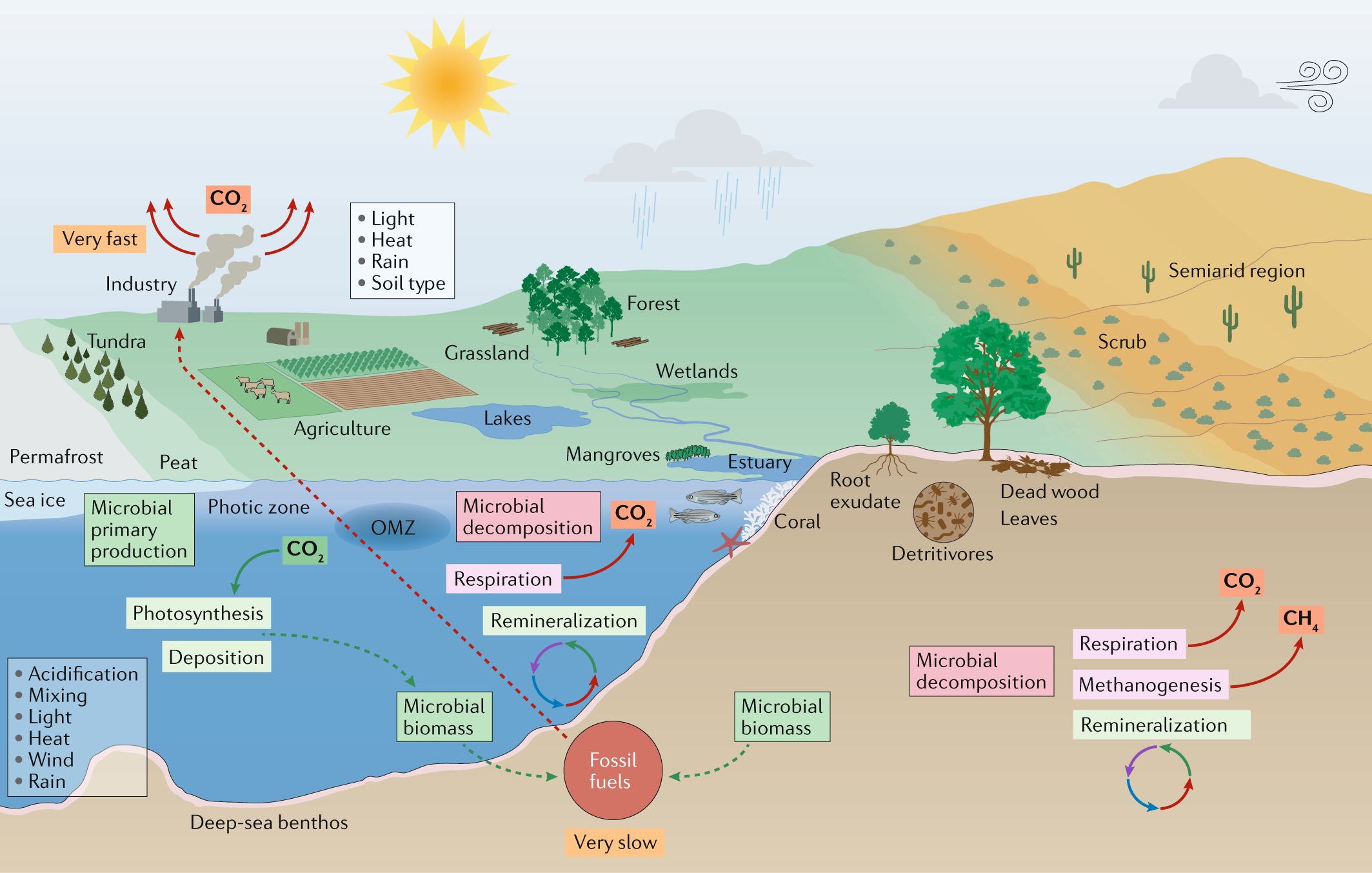
2c Carbon Cycle Feedbacks
The "greenhouse effect" is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, likeIt is Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Enhanced Greenhouse Effect listed as EGE Enhanced Greenhouse Effect How is Enhanced Greenhouse Effect abbreviated?First, let us tackle the first question What are the anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the first place?




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Higher Geography Global Warming Ppt Download
The ocean plays a central role in regulating the Earth's climate The Fifth Assessment Report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 13 revealed that it has thus far absorbed 93% of the extra energy from the enhanced greenhouse effect, with warming now being observed at depths of 1,000 m



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect By On Emaze
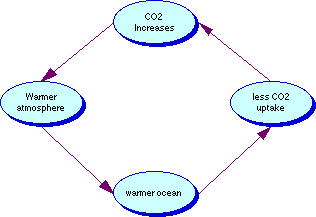



Climate Feedback Mechanisms And Human Response




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




The Causes Of The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And Assessment Of The Difficulties In Reducing Its Impacts International Baccalaureate Geography Marked By Teachers Com




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences
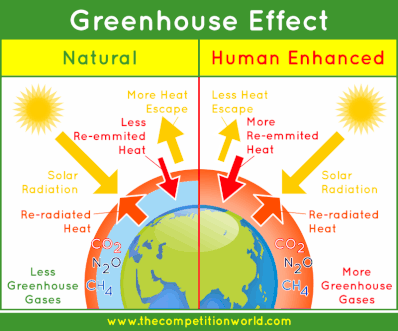



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green



Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Current Events For Kids Greenhouse Effect




Global Warming Giant Clams



1
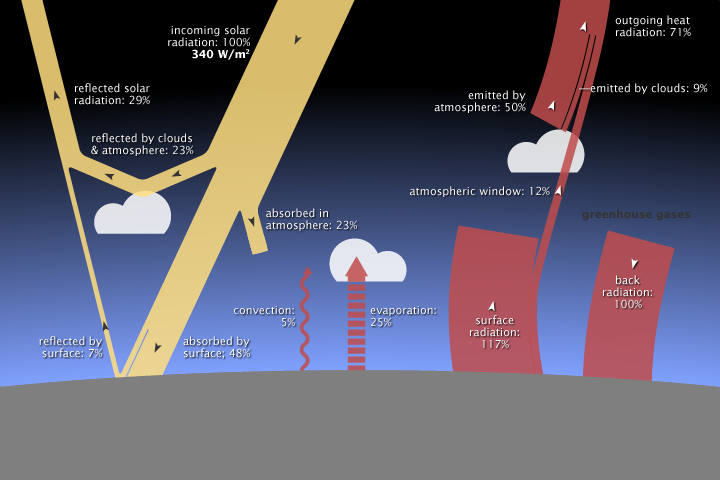



1 Causes Of Global Climate Change The Geographer Online




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Causes Of Climate Change



3




Global Warming




Teaching Climate Change American Federation Of Teachers




The Ocean And Climate Change Iucn




The Greenhouse Effect World101




The Causes Of The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And Assessment Of The Difficulties In Reducing Its Impacts International Baccalaureate Geography Marked By Teachers Com




Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet



A Natural Greenhouse Effect B Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
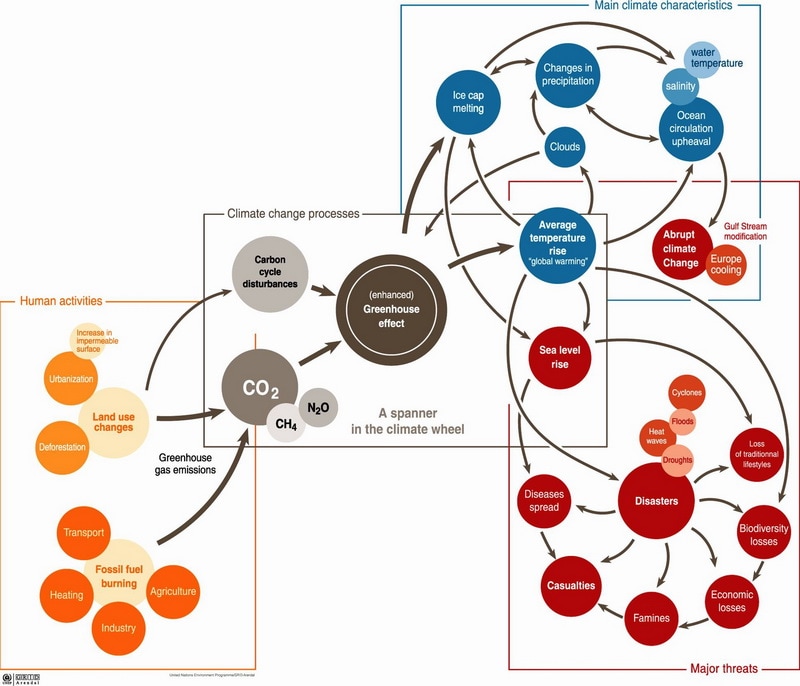



Ess Topic 7 2 Climate Change Causes And Impacts Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Global Warming 101 National Geographic Youtube



Climate Change Online Presentation




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Day 2 9 3 9 5 Ap Environmental




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Ib Geography Global Climate Vulnerability And Resilience Flashcards Quizlet



Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Ipcc Updates For Geography Teachers



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious



Canr Msu Edu



Global Climate Dp Geography Ib Recap



Scientists Warning To Humanity Microorganisms And Climate Change Nature Reviews Microbiology
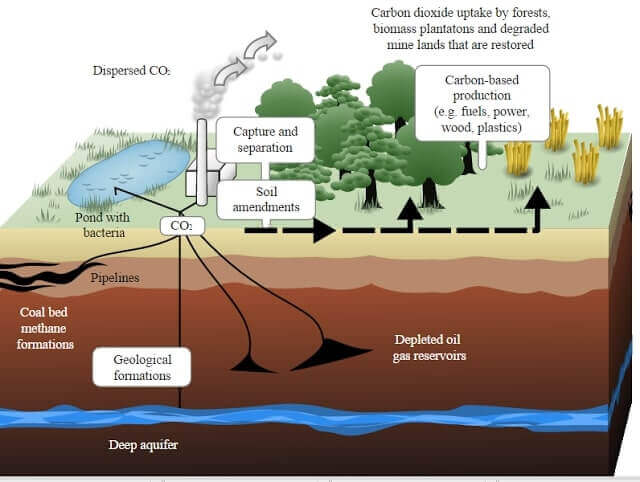



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias



Chewvalley Greenhousecms Co Uk



3 Weather And Climate Mrbgeography Introductions




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Geography A H 070 H 470 Topic Title



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect



Turton Uk Com
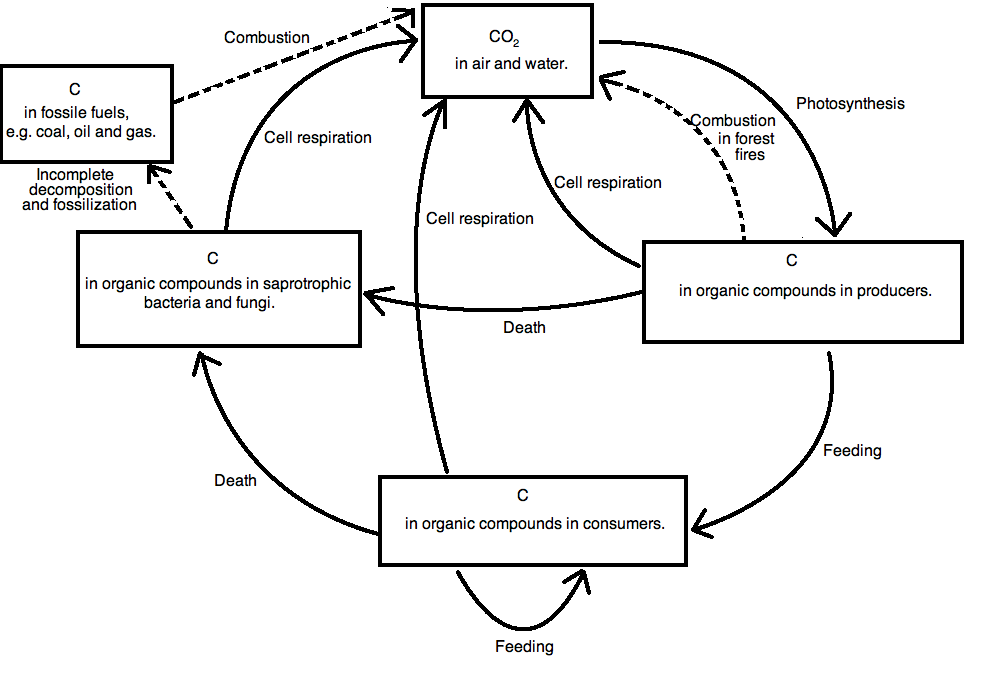



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect
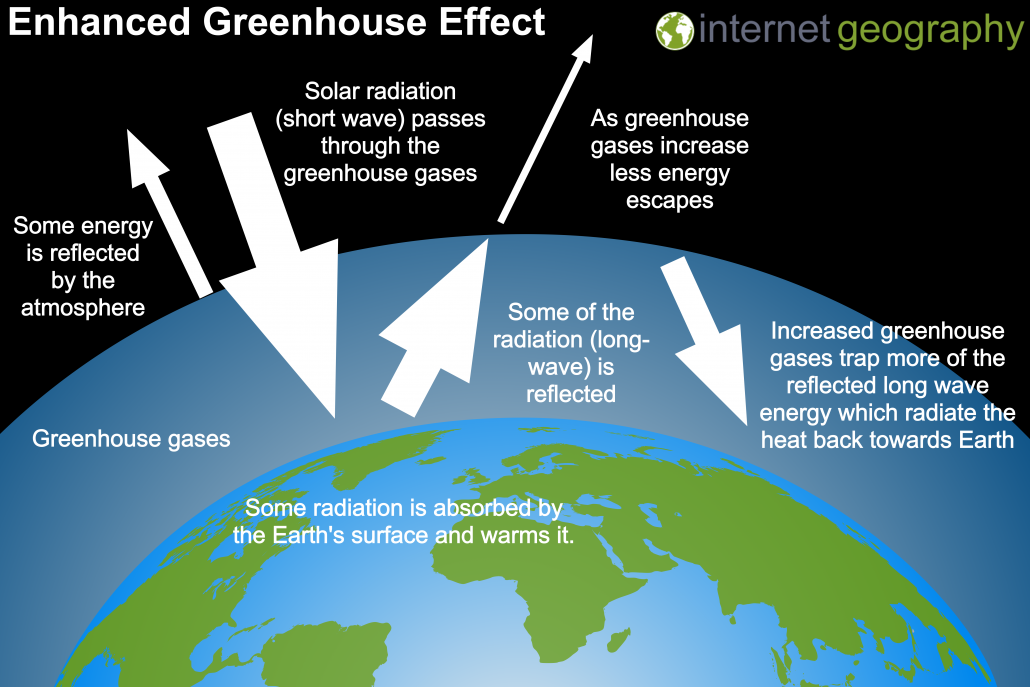



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography
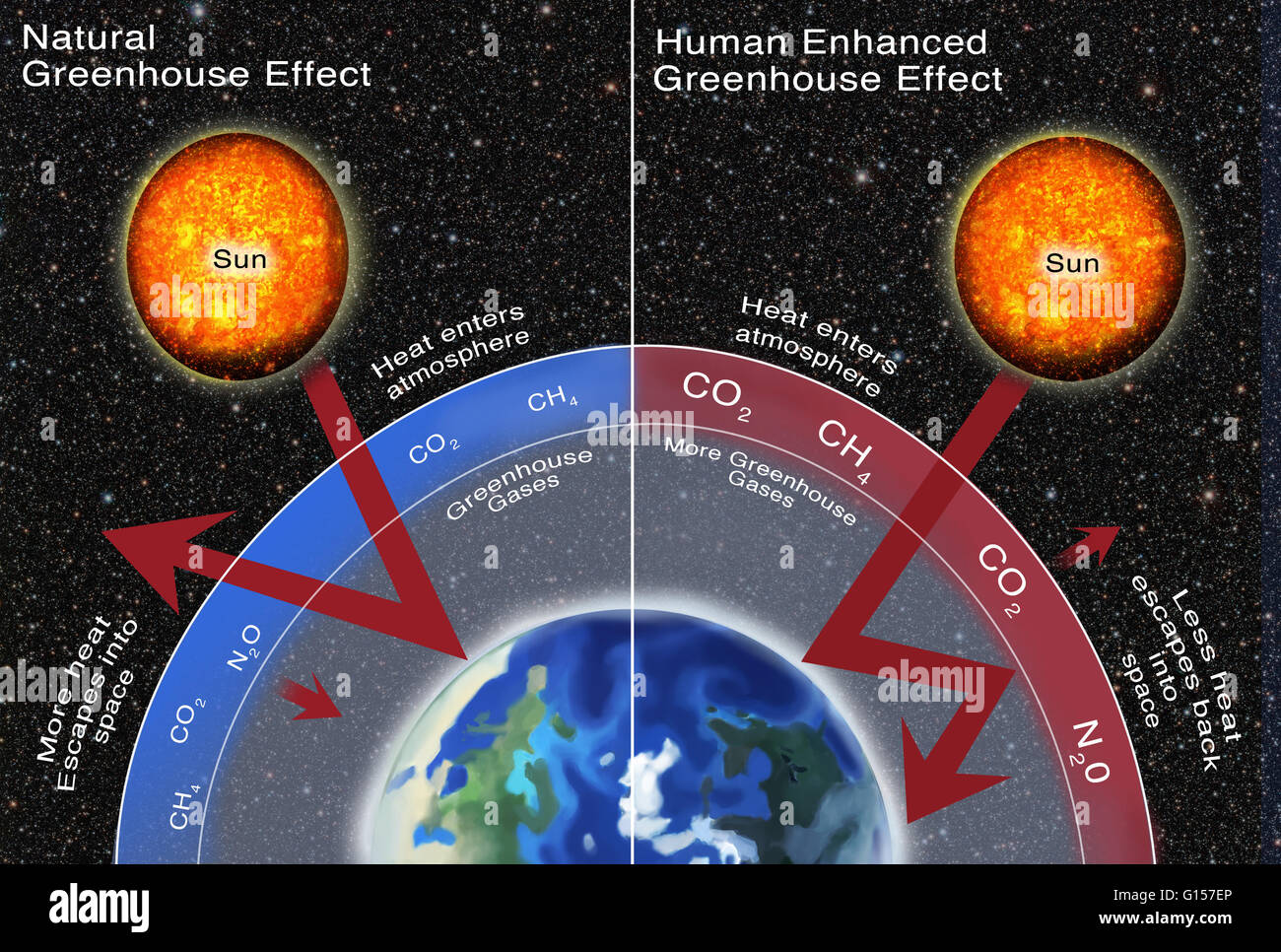



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
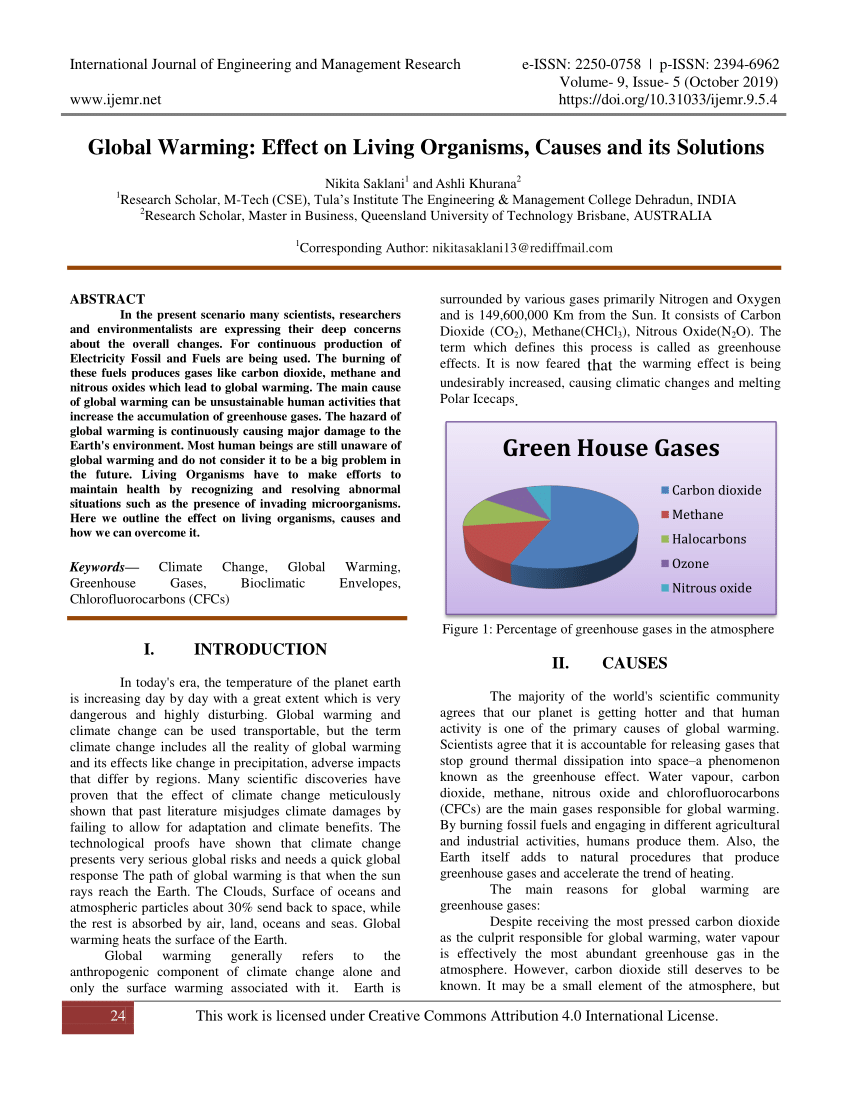



Pdf Global Warming Effect On Living Organisms Causes And Its Solutions




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change
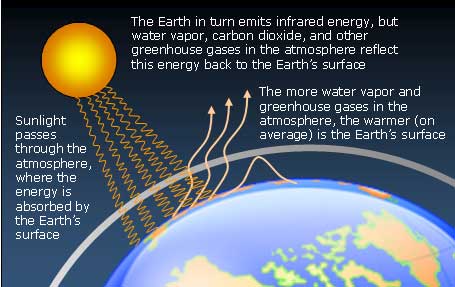



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious




Global Warming Has Increased Global Economic Inequality Pnas
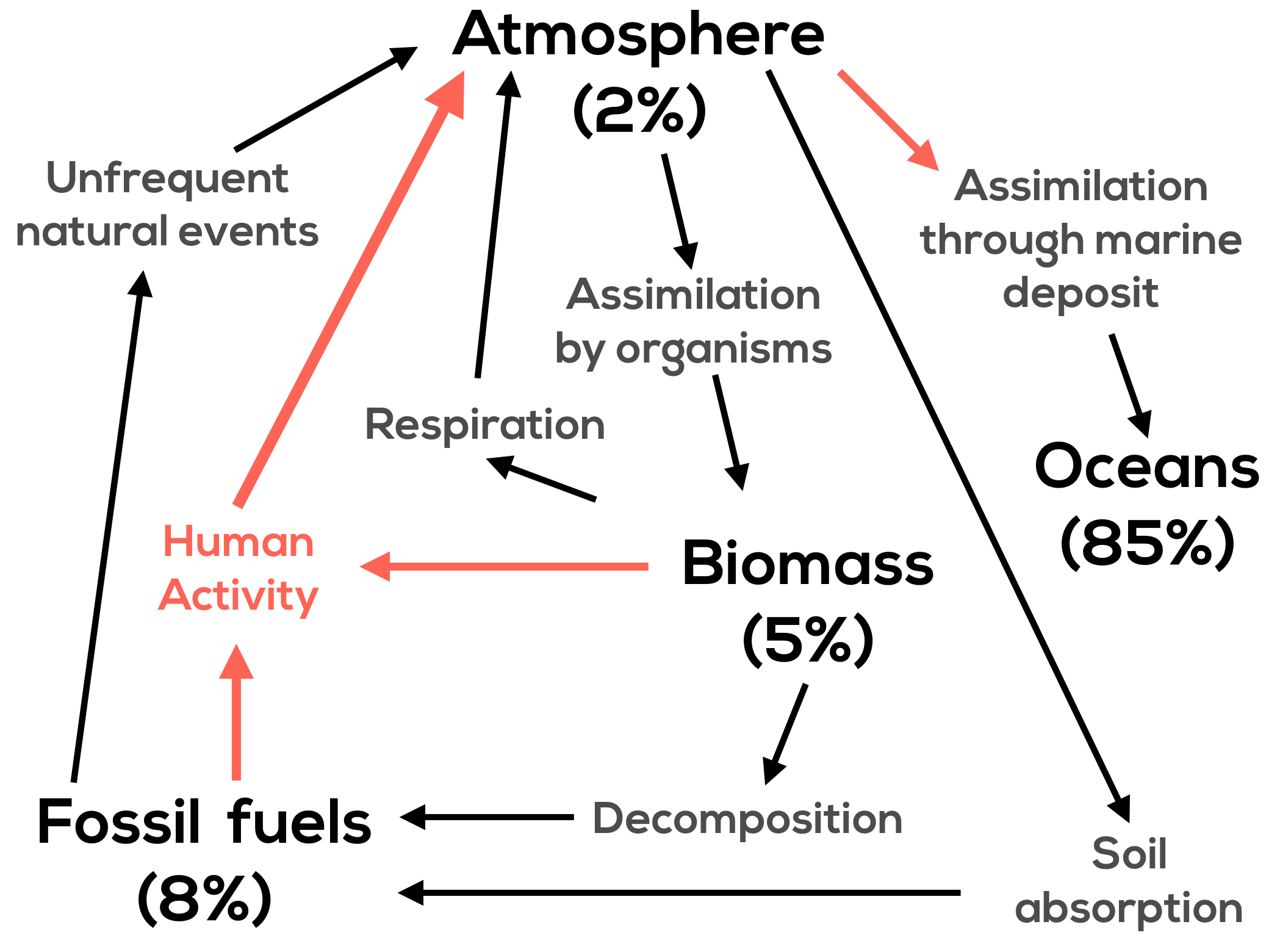



Global Climate Dp Geography Ib Recap
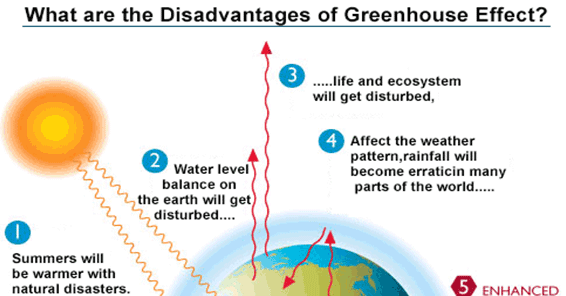



Disadvantages Of Greenhouse Effects Myassignmenthelp Com
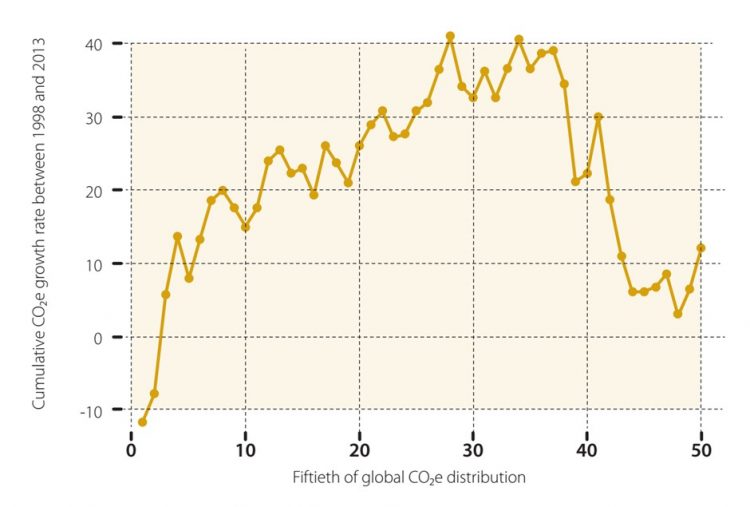



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp
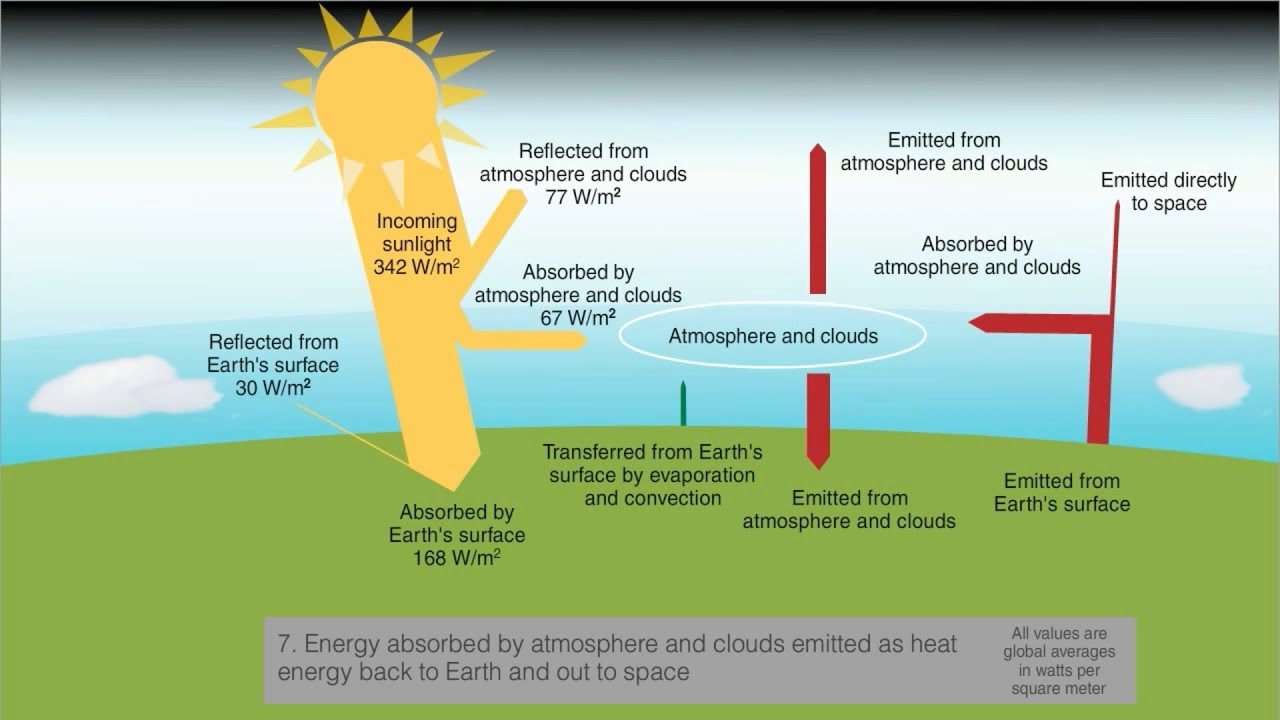



Atmosphere Change 4hrs Geography For 21 Beyond



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov




Influence On The Natural Greenhouse Effect A Level Geography Edexcel Revision Study Rocket




Gcse Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Geography Is Easy




Greenhouse Effect Definition And Synonyms Of Greenhouse Effect In The English Dictionary
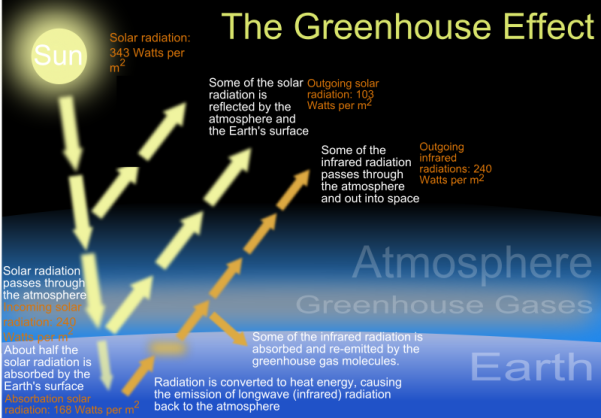



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
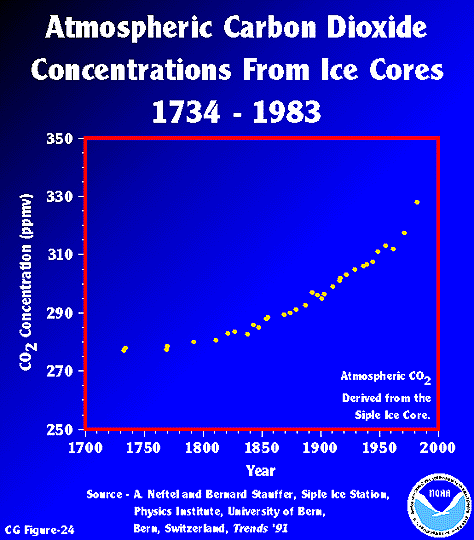



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Historical Evidence Of Global Warming Historic Global Temperatures The Chart Above Shows The Average Global Surface Temperature Every Year Since 10 The Data Is From Nasa S Goddard Institute For Space Studies To Understand Why The Earth Has Seen
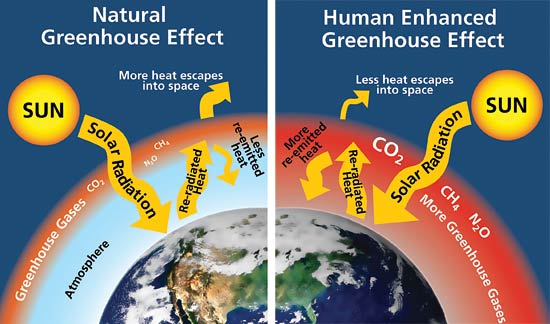



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




Geography Notes Ibo




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
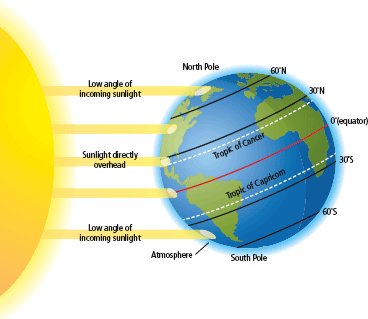



1 Causes Of Global Climate Change The Geographer Online



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
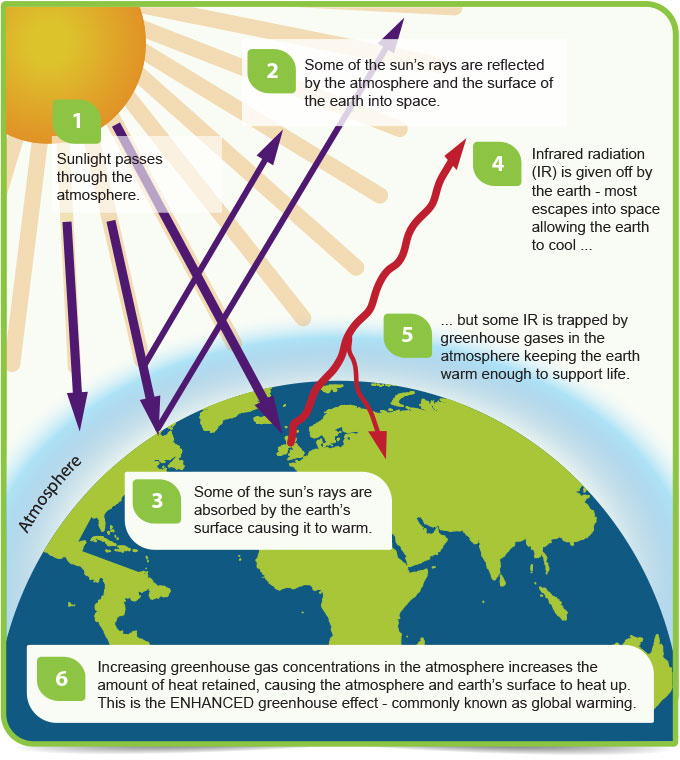



Changing Climate Scotland S Environment Web



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
コメント
コメントを投稿